Composite组合模式
what
桥接模式是一种结构型设计模式, 可将一个大类或一系列紧密相关的类拆分为抽象和实现两个独立的层次结构, 从而能在开发时分别使用。
why
组合模式的主要目的是使客户端对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性,同时也能够简化对复杂对象结构的操作。
structure
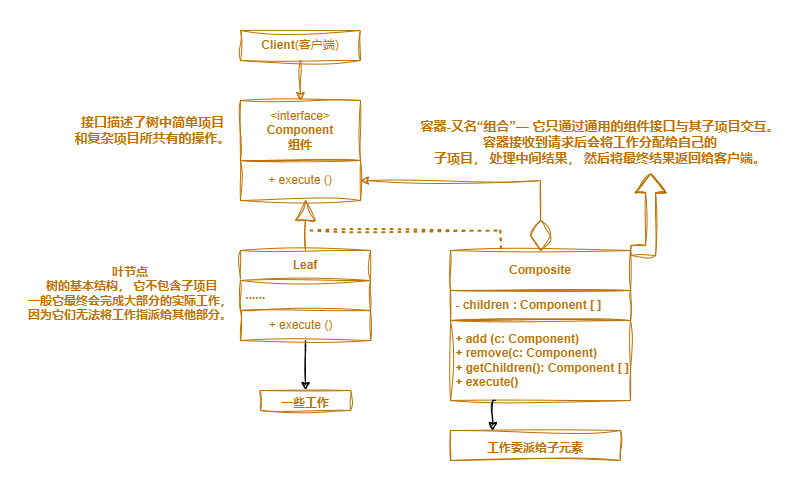
how
- 模型能够以树状展示
- 申明组件接口
- 创建叶子节点(简单元素)
- 创建容器节点(复杂元素)
- 容器可以添加和删除元素
// 组件抽象类
abstract class Component {
protected String name;
public Component(String name) { this.name = name;}
public abstract void display();
}
// 叶子节点类
class Leaf extends Component {
public Leaf(String name) { super(name);}
public void display() { System.out.println(name);}
}
// 树枝节点类
class Composite extends Component {
private List<Component> children = new ArrayList<Component>();
public Composite(String name) { super(name);}
public void add(Component component) { children.add(component);}
public void remove(Component component) { children.remove(component);}
public void display() {
System.out.println(name);
for (Component component : children) {
component.display();
}
}
}
// 客户端代码
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建树枝节点
Composite root = new Composite("root");
Composite composite1 = new Composite("composite1");
Composite composite2 = new Composite("composite2");
// 创建叶子节点
Leaf leaf1 = new Leaf("leaf1");
Leaf leaf2 = new Leaf("leaf2");
Leaf leaf3 = new Leaf("leaf3");
Leaf leaf4 = new Leaf("leaf4");
// 组合节点结构
root.add(composite1);
root.add(composite2);
composite1.add(leaf1);
composite1.add(leaf2);
composite2.add(leaf3);
composite2.add(leaf4);
// 调用统一的display()方法来处理节点及节点组合
root.display();
}
}
Leaf是叶子节点,没有子节点;Composite是树枝节点,可以包含叶子节点或其他树枝节点。Component是抽象类,定义了节点的通用操作,包括display()方法用于展示节点信息。
在客户端代码中,我们创建了一个树枝节点root以及两个叶子节点和两个树枝节点,然后通过add()方法将它们组合起来形成树形结构。最后,通过调用root的display()方法,可以递归地展示树形结构中的所有节点。
when
- 实现树状对象结构, 可以使用组合模式。
- 客户端代码以相同方式处理简单和复杂元素。
where
常用于表示与图形打交道的用户界面组件或代码的层次结构。
- java.awt.Container#add(Component) (几乎广泛存在于 Swing 组件中)
- javax.faces.component.UIComponent#getChildren() (几乎广泛存在于 JSF UI 组件中)
P&Cs
P:
- 利用多态和递归机制更方便地使用复杂树结构。
- 开闭原则
C:
- 功能差异较大的类, 提供公共接口或许会有困难。
summary
统一对待单个对象和对象组合,简化了对对象的操作和管理。
